Portable generators are incredibly handy tools, but keeping track of which fuel to use for each generator can be tricky. In this article, I’m going to demystify the different types of fuel used in portable generators: gasoline, propane and diesel. With this knowledge, you’ll have the power to make an informed decision about which generator is right for you and your needs.
I’m going to break down the pros and cons of each type of fuel so that you can make an educated choice on what kind of generator will best suit your needs.
We’ll also discuss how to store and transport the different fuels safely so that you can get the most out of your portable generator.
Ready to learn more? Let’s dive in!

Differences In Fuel Types
When it comes to portable generators, there are three main fuel types: gasoline, propane, and diesel. Understanding the differences between them can help you make an informed decision when choosing a generator for your needs.
Gasoline is the most common type of fuel used in portable generators due to its easy availability and relatively low cost. It is also fairly efficient and produces fewer exhaust fumes than diesel. However, it does have a few drawbacks; for example, due to its spark ignition system, gasoline-powered generators tend to be noisier than those powered by other fuels.
Propane has become increasingly popular in recent years because it has higher fuel efficiency than gasoline and produces fewer emissions. In addition, propane-powered generators are quieter than those powered by gasoline or diesel. The downside is that propane can only be stored in tanks at moderate pressures, making it more difficult to transport long distances.
Diesel is the least common of the three options but offers some advantages over gasoline and propane. Diesel engines are very reliable and require less maintenance than gasoline engines, making them ideal for extended use with minimal downtime.
Additionally, diesel engines generate less noise and produce lower levels of exhaust fumes than either gas or propane-powered units, so they’re better suited for enclosed spaces like garages or workshops. Despite these benefits, however, diesel is generally more expensive than other fuel sources and can be harder to find in some areas.
It’s important to weigh all of these factors carefully before deciding which fuel type works best for you; each one has its own advantages and disadvantages that should be taken into consideration when choosing a generator for your needs.
Pros And Cons Of Gasoline
Moving on from the differences between fuels, let’s look at the pros and cons of gasoline. Gasoline is a popular fuel source for portable generators because it is easier to find than propane or diesel, and it powers up quickly.
Let’s start with octane rating. High-octane gasoline produces more power when burned, but it also costs more money. If you’re looking to save a few bucks, you can opt for lower octane ratings. However, lower octanes are less efficient and may cause your generator to run less smoothly over time. It all comes down to what kind of performance you’re expecting from your generator and how much you’re willing to spend on fuel.
When it comes to cost comparison, gasoline tends to be cheaper than diesel or propane per gallon – but don’t forget about emissions effects! Gasoline generates more air pollution than either diesel or propane, so if that’s a concern for you then you should consider those other options instead.
Gasoline engines are also less fuel efficient than their diesel counterparts – meaning they burn through more fuel in the same amount of time – but they are compatible with most types of gasoline-powered equipment, making them an easy choice for most applications.
Finally, let’s take a look at the benefits of propane as an alternative fuel source.
Benefits Of Propane
Propane is a great alternative fuel source for portable generators, and it has several advantages to consider.
As a clean-burning fuel, propane is considered one of the most efficient sources to power a generator. Compared to gasoline, it’s easier to store because of its longer shelf life and fewer storage options. Propane can also provide cost savings due to its lower cost per gallon when compared to other fuels. Additionally, propane burns much cleaner than gasoline and produces significantly lower emissions levels.
When it comes to fuel efficiency, propane outperforms gasoline in many ways. It’s estimated that propane engines can produce up to 25 percent more power than gasoline equivalents while consuming up to 10 percent less fuel. This means that propane-powered generators will run longer with fewer fill-ups, saving you time and money in the long run.
Furthermore, due to its superior combustion quality, generators running on propane may experience fewer maintenance issues over their lifetime compared to those powered by gasoline or diesel.
In terms of safety, propane is also an excellent choice for portable generators because it’s non-toxic and doesn’t cause any environmental damage if spilled or released into the air.
Moreover, portable generators running on propane are usually quieter than those powered by gas or diesel due to their higher combustion efficiency and lack of exhaust noise. This makes them ideal for camping trips or any situation where you need reliable power without producing too much noise pollution.
The benefits of using a portable generator powered by propane are clear – from its cost savings and fuel efficiency to its ease of storage and clean burning nature – making it an ideal choice as an alternative source of energy for your next outdoor adventure or home emergency situation.
Ready for the next step? Let’s look at the advantages of diesel…
Advantages Of Diesel
Let’s take a closer look at the advantages of diesel generators.
For starters, diesel fuel is more efficient than gasoline or propane, meaning it can produce more power while using less fuel.
Diesel engines also have higher efficiency ratings than their gasoline and propane counterparts. This makes them an excellent choice for applications where output needs to be maximized with minimal energy expenditure.
Furthermore, diesel engines are often quieter than other types of portable generators, making them ideal for locations where noise levels need to remain low.
Lastly, diesel fuel is cleaner burning and more eco-friendly. It meets stricter emissions standards than gasoline or propane, which means it produces fewer pollutants into the environment and has better fuel economy overall.
Now that we’ve discussed the advantages of diesel fueled generators over other types of portable generators, let’s move on to consider storage options for fuel storage considerations.
Fuel Storage Considerations
When it comes to selecting the right fuel for your portable generator, there are a few things you need to keep in mind. Fuel selection criteria, storage requirements, fuel mixing, transport rules, and fuel quality are all important considerations.
If you’re using gasoline, you need to make sure it’s fresh and stored in an airtight container. It should be kept away from heat sources and stored in a cool area as heat can degrade its quality. You also need to make sure that you never mix different types of gasoline as this can cause problems with your generator.
Propane is an excellent option for portable generators as it’s safe and easy to use. Make sure that the propane tank is UL-certified, which means that it meets safety standards for pressure vessels. When transporting propane tanks, keep them upright and secure them in the vehicle so they don’t move around or fall over during transport.
Diesel fuel is a bit more complicated than gasoline or propane since it’s thicker and requires special handling procedures. Diesel must be free of dirt, water, or any other contaminants that could damage your generator engine. Be careful when transporting diesel as well – make sure it’s properly sealed in an approved container so no fumes escape into the environment.
Now that we’ve discussed the importance of selecting the right type of fuel for your portable generator and understanding its associated storage requirements, let’s take a look at availability and cost of these various types of fuel.
Availability And Cost Of Fuel Types
Now that you understand the considerations for storing your fuel, let’s talk about availability and cost of the different types.
When it comes to gasoline, you can easily find it at gas stations and convenience stores. It is relatively inexpensive, but you might want to consider getting a bulk delivery if you need multiple gallons for larger projects. Fuel additives and stabilizers are also helpful when storing gasoline since it tends to break down faster than other fuel types.
Propane is a bit more expensive than gasoline and usually not available in large quantities without special delivery services. If you plan on using propane as your primary generator fuel, you’ll want to invest in a bulk tank or get frequent deliveries from a local supplier.
You also need to remember that propane tanks require regular maintenance and inspection, as well as fuel filters if they are not already included with the generator model.
Diesel is another popular option for portable generators because of its ability to store well over long periods of time without breaking down like gasoline does. However, diesel can be expensive and hard to come by in smaller quantities.
You will likely need to get a bulk delivery from a local supplier or purchase it from truck stops when traveling with your generator.
Now that you know about availability and cost of these three fuel types, it’s important to learn about their shelf life so you know how often they should be replaced or replenished.
Shelf Life Of Portable Generator Fuels
When it comes to keeping your generator running in peak condition, it is important to understand the shelf life of the fuel you are using. Fuel aging, fuel additives, fuel storage, fuel blending and fuel contamination can all impact the longevity of your portable generator’s fuel supply. To help you assess the best approach to maintaining your generator’s fuel supply, I have created a table below that outlines each type of generator fuel and its associated shelf life.
| Fuel Type | Shelf Life | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Gasoline | 3-6 months | Store in an airtight container away from heat sources & sunlight. Avoid mixing with other fuels or additives. |
| Propane | 1-3 years (if stored properly) | Store in an airtight container away from heat sources & sunlight. Avoid mixing with other fuels or additives. May require pressure relief valve for propane tanks above 40lbs. |
| Diesel | 6-12 months (if stored properly) | Store in an airtight container away from heat sources & sunlight. Avoid mixing with other fuels or additives. Use a specialized diesel stabilizer additive to extend shelf life up to two years when stored correctly. |
It is important to note that improper storage of any type of generator fuel will decrease its shelf life significantly and may even cause damage to your portable generator due to contamination or degradation of the fuel itself over time.
Taking extra precautions such as maintaining a regular maintenance schedule and using only fresh, high quality fuels will extend the lifetime performance of your portable generator for many years without fail.
With this knowledge about the shelf life and storage requirements for each type of portable generator’s respective fuels, we can now move onto learning about their maintenance requirements for optimal performance.
Maintenance Requirements Of Generator Fuels
Maintaining a portable generator can be essential to its longevity and performance. It is important to understand the requirements of each fuel type, as they all have their own unique maintenance needs. Gasoline, propane, and diesel are the three most common types of fuels for portable generators. Each have their own drain intervals, fuel filtration needs, fuel additives, exhaust fumes considerations, and potential risks associated with fuel mixing.
When it comes to maintaining your generator’s gasoline tank, there are several things you should know. First and foremost, gasoline should be stored in an airtight container at room temperature. Additionally, it’s important to always check for water or debris when filling up your tank.
This can help prevent corrosion and other damage. Also keep in mind that gasoline has a shorter shelf life than diesel or propane – typically only five months or so – so you may need to replace it more frequently if it isn’t used often enough.
Propane generators require slightly different maintenance procedures than gasoline generators do. For one thing, they don’t need to be filled up as often since propane is stored in tanks that last longer than regular gas tanks do.
However, when refilling your propane tank you should always make sure there are no leaks before doing so. Additionally, filters must be changed regularly to ensure the generator runs properly and doesn’t emit any dangerous exhaust fumes.
Diesel generators require much less frequent refueling than either gasoline or propane generators do; however they also tend to produce stronger exhaust fumes when running due to the higher viscosity of diesel fuel compared with other fuels like gasoline or propane.
Because of this it is important to keep your diesel generator well-maintained by changing the oil regularly and checking for any buildup of dirt inside the engine itself which can cause clogs in the fuel system over time if left unchecked.
Additionally, you should use only high-grade diesel fuel additives specifically designed for use in diesel engines when refilling your tank.
Keeping up with maintenance for your portable generator is key for ensuring its longevity as well as preventing any potential risks associated with using a malfunctioning machine such as fire hazards or carbon monoxide poisoning from faulty exhaust systems.
Knowing how best to maintain each type of fuel will ensure that your generator runs smoothly and safely every time you need it – no matter what type of fuel you choose!
With this knowledge under our belts we can move on to understanding safety precautions when using portable generators.
Safety Precautions When Using Portable Generators
Using a portable generator is a convenient way to get power when you need it. But there are some important safety precautions you should take before operating one.
Fuel handling rules, exhaust emission, fuel spill prevention, noise control, and fuel testing are all things to consider.
When dealing with combustible fuels like gasoline and propane, it’s essential to be aware of how these fuels can interact with the environment. It’s important to store them in an area that is well ventilated and away from any sources of heat or ignition. If the generator has been running for a while, allow it to cool down before refueling it. And never attempt to refill the tank while the engine is running.
You also want to make sure that your generator produces as little emissions as possible by maintaining it regularly and ensuring that the fuel lines are always clean. In addition, use proper noise-control strategies such as installing mufflers or keeping generators far away from inhabited areas if possible. Lastly, test your fuel periodically for quality assurance since poor quality fuel can cause expensive damage over time.
The care you take when using portable generators isn’t just about protecting yourself; it’s about taking responsibility for the environment too. As we move on to discuss the environmental impact of portable generator fuels, remember that our actions have consequences that extend beyond ourselves.
Environmental Impact Of Portable Generator Fuels
Now that we’ve discussed the safety precautions to consider when using a portable generator, let’s explore the environmental impact of different types of fuel.
Gasoline, diesel and propane are all common options for powering portable generators, but it’s important to understand how each type of fuel impacts our environment. Each has distinct advantages and disadvantages in terms of air quality and carbon footprint.
When it comes to emission regulations, gasoline is a less desirable option. Gasoline-powered engines produce more emissions than diesel or propane-powered engines, creating pollutants that can have negative effects on air quality. They also tend to be less fuel-efficient than diesel or propane-powered generators, resulting in higher costs and greater energy consumption over time.
Propane-powered generators offer several advantages over gasoline and diesel models. Propane is less expensive than gasoline or diesel and produces fewer emissions, making it an attractive choice for those concerned about their carbon footprint. It’s also more efficient than either diesel or gasoline, meaning it can help save you money in the long run with its greater fuel economy.
No matter which type of fuel you decide to use for your portable generator, understanding the implications of your decision can help ensure you make the best possible choice for both safety and sustainability purposes. Choosing the right fuel for your generator can help keep you safe while reducing your environmental impact at the same time!
Choosing The Right Fuel For Your Portable Generator
When you’re deciding on the right fuel for your portable generator, there are a few key factors to consider: fuel stability, noise levels, fuel efficiency, fuel compatibility, and cost comparison. Let’s take a look at how gasoline, propane and diesel stack up against each other.
| Fuel Type | Fuel Stability | Noise Levels | Fuel Efficiency | Fuel Compatibility | Cost Comparison |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gasoline | Moderately Stable | Moderate/High | Low/Moderate | Widely Available | Lowest Cost |
| Propane | Extremely Stable | Low/Moderate | High Efficiency | Limited Availability | Moderate Cost |
| Diesel | Low/Moderate | Widely Available |
Gasoline is the most widely available option when it comes to portable generator fuels. It has a moderate level of stability and moderate to high noise levels, but it is relatively inexpensive compared to other options. The downside is that its fuel efficiency is low to moderate.
Propane offers excellent fuel stability and low-moderate noise levels while providing higher efficiency than gasoline. However, propane may not be as readily available as gasoline or diesel in some locations and tends to be more expensive than other options.
Diesel offers lower noise levels than gasoline and is widely available in most places. However, due to its higher cost it might not be the most economical option for everyone’s budget. Additionally, diesel has a limited compatibility with some portable generators models so make sure you check before investing in this type of fuel.
In summary, when selecting the right fuel for your portable generator it’s important to compare different factors such as fuel stability, noise levels, fuel efficiency and cost – all of which vary depending on the type of fuel you choose. All three options have their own advantages and disadvantages so take your time researching what works best for you before making your decision!
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Best Type Of Fuel To Use For A Portable Generator?
When it comes to portable generators, each type of fuel has its own pros and cons.
Gasoline is usually the cheapest option, making it a great choice for those on a budget.
However, propane has the benefit of being more efficient and having higher fuel quality.
Diesel is also known for its efficiency but can be more expensive than gasoline and may not be as easy to find in certain areas.
Fuel compatibility should also be taken into consideration; some models may require a specific type of fuel, so make sure you know what your generator needs before making your purchase.
Ultimately, the best type of fuel to use for a portable generator depends on your budget, availability, efficiency needs, and compatibility with your model.
How Long Can A Portable Generator Fuel Be Stored?
When it comes to storing fuel for a portable generator, it’s important to keep in mind the fuel properties and storage regulations.
Temperature is an important factor when it comes to fuel longevity; for example, diesel can be stored for up to 12 months if the temperature remains consistent.
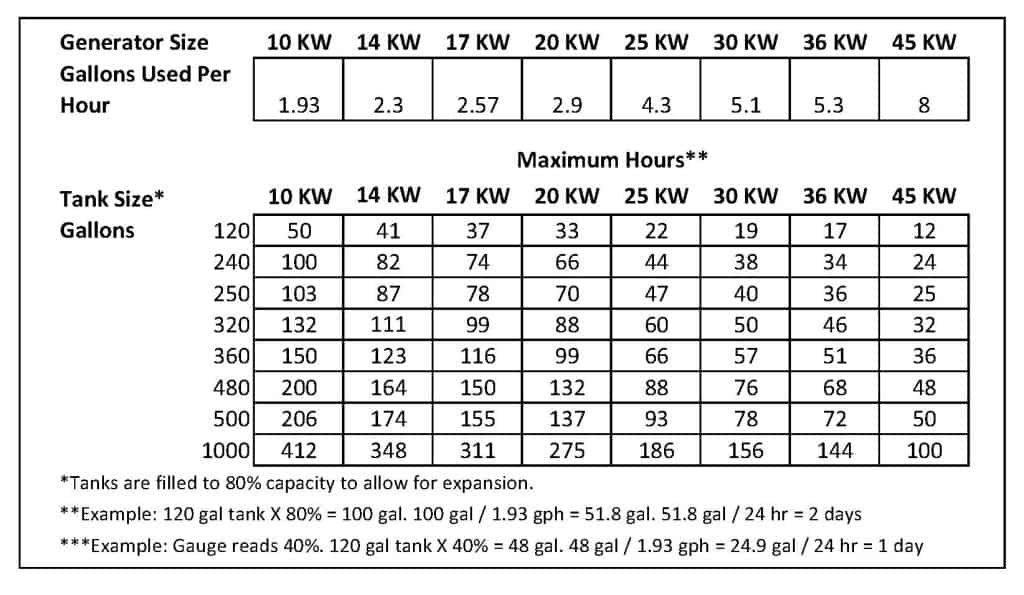
Gasoline and propane, on the other hand, have shorter storage life spans; gasoline typically lasts 3-6 months while propane can last up to 1 year.
It’s always best to check with local fuel regulations before storing any type of fuel for long periods of time.
Are There Any Safety Measures To Take When Using A Portable Generator?
Using a portable generator is no joke – it’s important to take safety measures to ensure you’re using it properly and safely.
Start by making sure your generator is properly ventilated – never use it indoors or in an enclosed area.
Also, be mindful of fuel spillage and noise pollution. Ensure you select the right fuel for your machine and make sure to store any leftover fuel safely.
Lastly, factor in fuel costs when selecting the right generator for you.
With the right knowledge and safety measures in place, you can easily master the art of using a portable generator!
Does The Type Of Fuel Used For A Portable Generator Affect Its Maintenance Requirements?
No matter what type of fuel you use for your portable generator, you’ll need to think about the cost, shelf life, smell, hazards and emissions it can produce.
Gasoline has a short shelf life but is generally cheaper than propane or diesel. It also has a strong smell and can be dangerous if not handled properly.
Propane is great for cold weather as it’s less likely to freeze than gasoline.
Diesel fuel is the most expensive option but has a longer shelf life compared to gasoline and propane. The emissions from diesel are usually lower than other fuels so it may be better for the environment.
All these factors should be taken into consideration when deciding which fuel to use in your portable generator and how often you’ll need to maintain it.
Does The Type Of Fuel Used For A Portable Generator Have An Environmental Impact?
When it comes to the environmental impact of a portable generator, there are a few things to consider.
Fuel emissions comparison, fuel economy, fuel storage solutions, fuel handling precautions, and fuel compatibility all play important roles.
Gasoline-powered generators produce more emissions than propane or diesel models.
Propane offers better fuel economy and is easier to store and handle safely.
Diesel is one of the most efficient fuels available and requires less maintenance than gasoline-powered generators, but it’s not compatible with all generator models.
If you’re looking for an eco-friendly option that won’t sacrifice performance or convenience, consider researching each type of fuel before making your decision.Maximizing Power: Fuel Efficiency In Portable Generators
Conclusion
It can be confusing to decide which type of fuel is best for a portable generator. Ultimately, the type of fuel used will depend on personal preference and needs.
Depending on the circumstances, gasoline, propane or diesel may be the most appropriate choice. However, regardless of which type of fuel is chosen, it’s important to take safety precautions when using a portable generator and to remember that the type of fuel used will have an impact on maintenance requirements and environmental considerations.
With proper research and preparation, you can make an informed decision about which fuel is best for your portable generator.



